A comparative study of AI and human programming on environmental sustainability
Original Article Summary
Scientific Reports - A comparative study of AI and human programming on environmental sustainability
Read full article at Nature.com✨Our Analysis
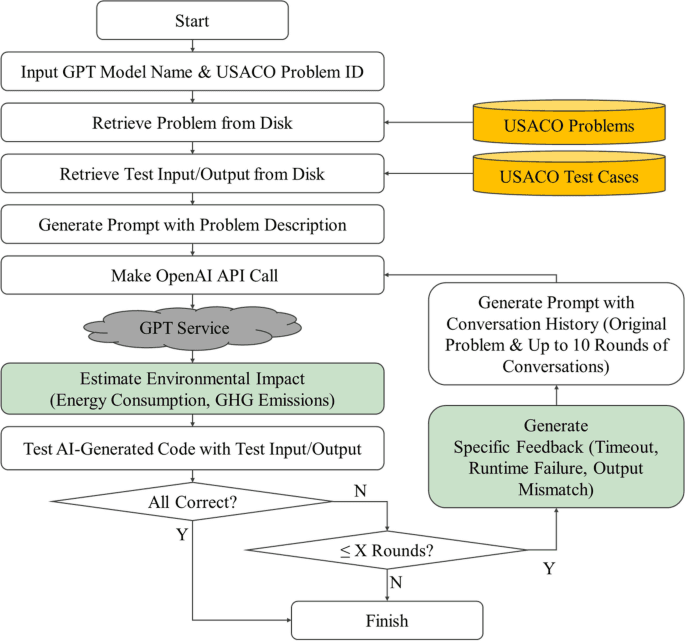
Scientific Reports' publication of a comparative study on AI and human programming on environmental sustainability highlights the growing importance of assessing the environmental impact of coding practices. This study's findings have significant implications for website owners, as they underscore the need to consider the environmental sustainability of their online platforms. With the increasing awareness of environmental issues, website owners must be mindful of the carbon footprint of their websites, including the energy consumption of AI-powered components. The study's comparison of AI and human programming practices can inform website owners' decisions on how to optimize their website's environmental sustainability, potentially influencing their choice of programming languages, software frameworks, and hosting services. To mitigate the environmental impact of their websites, website owners can take actionable steps such as monitoring AI bot traffic to identify areas of high energy consumption, optimizing their llms.txt files to reduce unnecessary AI-powered requests, and exploring eco-friendly web hosting options that prioritize renewable energy sources. By doing so, website owners can contribute to a more sustainable digital landscape while maintaining the performance and functionality of their online platforms.
Track AI Bots on Your Website
See which AI crawlers like ChatGPT, Claude, and Gemini are visiting your site. Get real-time analytics and actionable insights.
Start Tracking Free →

